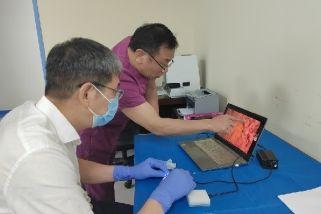
BEIJING, Dec. 31 (Xinhua) -- The Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in east China's Zhejiang Province has recently released a Compact Disposable EndoCytoscope (CDEC) at a conference on high-quality development of hospitals held in Quzhou, marking a breakthrough in solving the optical biopsy problem.
The device is expected to improve the accessibility of high-quality medical care in underdeveloped areas, and promote global medical equity.

Endoscope is an important tool for doctors to observe the inside of the human body. There are as many as 225-250 million endoscopic surgeries performed worldwide every year.
The concept of optical biopsy was proposed dozens of years ago, aiming to achieve tissue diagnosis through optical means and avoid the cumbersome steps and potential medical risks of traditional biopsy methods.
The CDEC was invented and developed by a team led by Everest Imaging, LLC, the Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University and City University of Hong Kong. The team achieved ultra-high image resolution while significantly reducing manufacturing costs. CDEC is expected to applied in various clinical specialties in 2 years.
Featuring one-step visual imaging that mimics direct observation with the naked eye, CDEC offers immediate clinical applications and promises paradigm shift for the optical biopsy, complementing traditional biomedical imaging techniques such as MRI and CT. CDEC also creates a new field of study in fundamental medicine and biology, particularly facilitating real-time, in-situ, in-vivo study of subcellular and cellular behaviors in cancer research. The team is going to present the CDEC technology at 2025 SPIE BIOS Endoscopic Microscopy in San Francisco in January 26-27. (Edited by Gu Shanshan with Xinhua Silk Road, gushanshan.1987@163.com)




 A single purchase
A single purchase