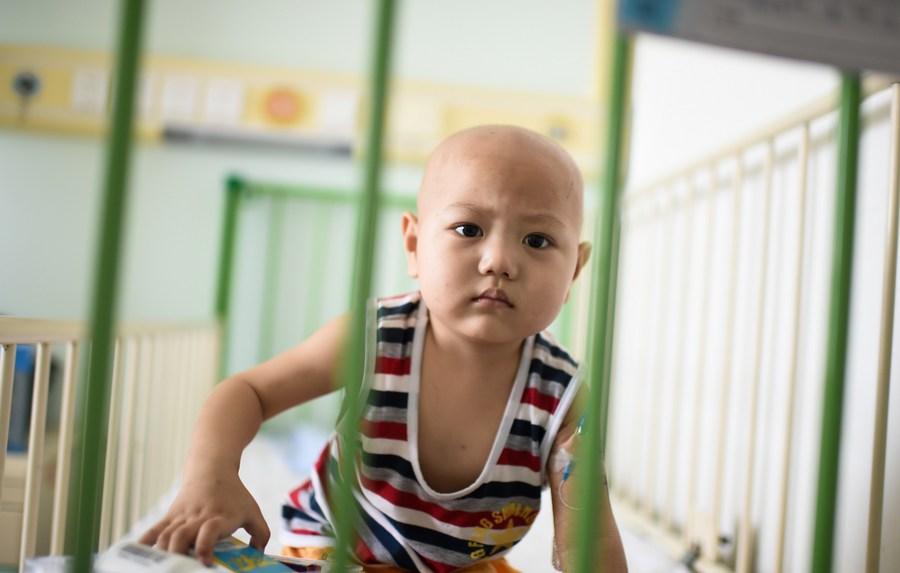
A two and half years old child with leukemia was hospitalized in Tianjin, north China, on May 31, 2017. (Xinhua/Bai Yu)
BEIJING, Jan. 27 (Xinhua) -- Chinese scientists developed a new potential therapy to treat leukemia, a disease that kills about 300,000 globally every year.
The study published Thursday in the journal Science Translational Medicine showed that injecting nanoparticles carrying a certain gene segment could effectively clear those blood cancer cells in an animal model.
An abnormal cellular energy metabolism was previously known to be linked to leukemia, but it is unclear which is the cause and which is the effect.
The research team from Jinan University in south China's Guangdong Province revealed that the changes in metabolism prompted the normal blood-producing stem cells into leukemia-initiating cells.
They found that the loss of the expression of a microRNA called miR-31-5p altered the way cells utilize energy, thus producing a metabolite called fumarate which led to the development of leukemia.
MicroRNA is a class of small single-stranded non-coding RNAs that play important roles in regulating gene expression.
The researchers developed a potential drug composed of nanoparticles encapsulating this piece of microRNA. It inhibited progression of acute myeloid leukemia disease in a mouse transplanted with human leukemia cells, causing no side effect, according to the study.
Yan Daoguang, a professor of tumor molecular biology at Jinan University who led the study, said the study helped extend the understanding of the origin mechanisms of blood cancer cells and suggested a new option for the treatment of leukemia.




 A single purchase
A single purchase