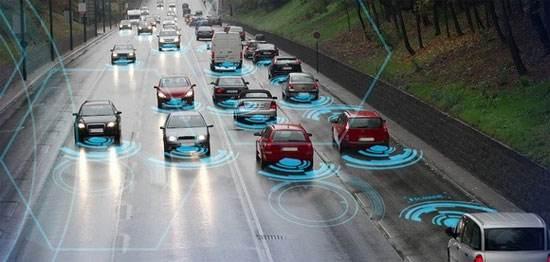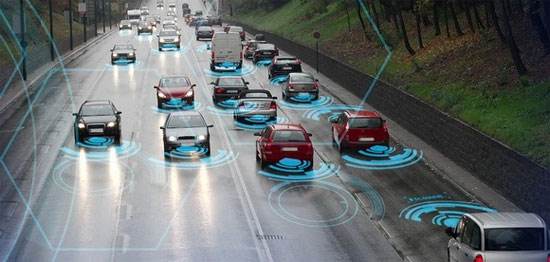
BEIJING, Jan. 18 (Xinhua) -- China's automotive industry is undergoing an unprecedented transformation, with more government supports for intelligent and environmental-friendly automotive technologies.
Following a series of key documents on setting up standards and preparing conditions for the new energy vehicles(NEV) and intelligent cars released in 2018, China is expected to quicken its pace to enter the green and intelligent era in 2019.
-- Intelligent development becomes a strategy
China unveiled a strategic plan for intelligent vehicle innovation development in January 2018, which spans more than 15 years.
According to the plan, by 2020, intelligent vehicles would account for 50 percent of the new automotive vehicles, and the coverage of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) network would reach 90 percent in large cities and highways. By 2025, almost every new automobile will be intelligent with large-scale application of intelligent technologies in highly-sophisticated ones. At that time, the new generation of vehicle network, 5G-V2X, will basically meet the demands.
In long term run, China is expected to develop into a global leading force in this area, and create a safer, greener and more efficient lifestyle for people in the country by 2035.
The plan also stipulates that by 2020, the proportion of independent brands in the intelligent car market reaches 30 percent.
-- More road test for ICVs allowed
From April 2018, local governments in China are allowed to arrange road tests for intelligent connected vehicles (ICVs). Local regulators can decide the road section available for tests, take test applications and issue test car plates, according to the regulations released by the country's ministries of industry and information technology, public security, and transport.
The ICVs, or connected cars, which can be connected to the internet, or with other vehicles, traffic, and the environment, cover different degrees of autonomous driving.
The regulations also specify requirements for test applicants and vehicles. Closed-area tests should be taken first before the vehicles are tested on normal roads.
Many automobile makers as well as internet companies are investing in connected cars, which they believe will become popular in the near future.
China issued its first batch of car plates for road tests of connected cars in Shanghai on March 1, 2018, followed by other cities such as Beijing, Chongqing, and Pingtan, Fujian Province.
-- Subsidy cut to stimulate innovation in NEVs
In recent years, China has intensified efforts to encourage the use of NEVs to ease pressure on the environment by offering subsidies, tax exemptions and discounts for car purchases.
As the industry now grapples with overcapacity and high inventories, the government has released stricter subsidy rules to press automakers and battery manufacturers to upgrade technology and push forward the NEV industry.
Starting June 12, 2018, NEV with a driving range below 150 km will not receive subsidies, those with a 150 km to 300 km driving range will receive minimal subsidies, and those with over 300 km will receive the most, according to the policy released by the Ministry of Finance.
Battery power/weight requirements for receiving subsidies have also been increased from 90 wh/kg to 105 wh/kg.
The newly-implemented subsidy policy for new energy vehicles (NEVs) will aid the industry's high-quality development and avoid low levels of blind expansion.
The strong wind of auto industry transformation is likely to blow into the new year of 2019, and a modernized era where highly-intelligent cars become commonplace is coming nearer.
-- FDI threshold to disappear in auto industry
In the past year of 2018, China's automobile industry welcomed a new round of opening up, which attracted global attention.
In April 2018, China's top economic planner, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), decided to cancel the restriction on foreign shares in all car companies within five years, a big gesture to guide more foreign investment into the country's auto industry, which will inject energy into the rising auto sectors.
The NDRC set up different timelines for different types of vehicles. For special-purpose vehicles and NEV, the restriction was to be canceled by 2018; for commercial vehicles, 2020; and for passenger vehicles, 2022. Meanwhile, the limit which bans foreign companies to set up more than two joint ventures in China will also be cancelled by 2022.
Specially, the official cancellation of the restriction on foreign investment in NEV began on July 28, 2018, when the Negative List, which widens market access for foreign investment, went into effect.
Electric carmaker Tesla became the first beneficiary of this policy, which established its first overseas factory in Shanghai with a designed annual production capacity of 500,000 units. Cars to be produced in the factory will include the famous Model 3. (Edited by Li Wenxin)




 A single purchase
A single purchase